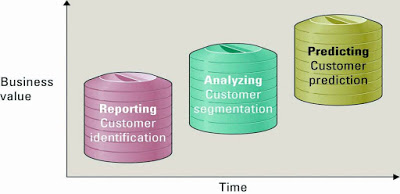
CHAPTER 11 - BUILDING A CUSTOMER CENTRIC ORGANIZATION - CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT ADVANTAGES OF CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP MANAGEMENT provide better customer service make call centers more efficient cross sell products more effectively helps sales staff close deals faster simplify marketing and sales processes discover new customers increase customer revenues RECENCY, FREQUENCY, AND MONETARY VALUE Recency - how recently a customer purchased items Frequency - how frequently a customer purchased items Monetary value - how much a customer spends on each purchase EVOLUTION OF CRM CRM reporting technology - help organization identify their customers across other applications CRM analysis technologies - help organization segment their customers into categories such as best an worst customer CRM predicting technologies - helps organizations make predictions regarding customer behavior such as which customers are at risk o



.jpg)